Access level: read, write
This connection enables data retrieval from web services that apply the REST (representational state transfer) architectural style. Such "RESTful APIs" are widely used by a variety of service providers.
The REST connection supports REST web services that
- are based on HTTP
- use the HTTP methods GET, PATCH, POST, DELETE, and PUT
- return data in either JSON or XML format
The REST connection supports the SSL protocol, i.e. HTTPS URLs are allowed. No special parameters are required for its use.
Notes:
- For returned data, only application / xml and application / json are allowed. Content types such as text / plain, text / html, image / gif and image / jpeg are not allowed.
- Only connections with HTTP modes GET and POST are possible for JSON and XML extracts. During a data preview of the extract, the POST request is executed, which may provoke undesired changes on the service endpoint.
- Testing a REST connection with HTTP mode PATCH, POST, PUT, or DELETE only tests the reachability of the host via HEAD request.
- For REST connections with HTTP mode POST, PUT, PATCH, or DELETE, the default encoding of a request body is UTF-8. If the web service only accepts requests with the body encoded in ISO-8859-1, you can add
; charset=iso-8859-1to the Content-Type header, liketext/xml; charset=iso-8859-1.
Preemptive authentication
The Integrator REST connection can support authentication in a "preemptive" manner, meaning that the client sends authentication information when initially establishing the connection, without getting challenged for it. This feature is especially useful for using S/4 Hana web services to provide S/4Hana CDS views.
REST and OAuth2Token connections: limitations
When a REST connection is used as a global connection, and it uses a global OAuth2Token connection as authentication method, there are some limitations.
- The REST connection cannot be tested in the Connections Manager. However, both the OAuth2Token and REST connections can be tested in the Integrator component.
- In the Connections Manager, the combo box for the OAuth2Token connection will not work.
- The global OAuth2Token connection must have the same name as the link to it in the Integrator UI.
REST connection with XML/JSON load
For XML loads or JSON loads using a connection type REST, the REST connection must use HTTP methods PATCH, POST, PUT, or DELETE. The data may be static or filled dynamically during the load.
Dynamic data: in this case, the request body of the REST connection is filled dynamically during the load with the data generated by the XML/JSON load. Therefore, the REST connection must have an empty request body in its definition.
Static data: in this case, the XML/JSON load must not have a data source assigned. The load simply executes the HTTP call as defined in the REST connection.
Connection settings
| Resource | The URL for the source data, e.g. https://abc.example.com/resource. |
| HTTP method | GET: retrieves a resource but does not modify it in any way (read only). This method is cacheable. GET requires a URL parameter (see below).
POST: creates a new subordinate resource, such as a subdirectory. This method requires a Header Parameter (see below) or Request Body (see Advanced Settings). PUT: replaces an existing resource or creates a new resource if it does not already exist. DELETE: deletes a resource. PATCH: makes partial changes to an existing resource. |
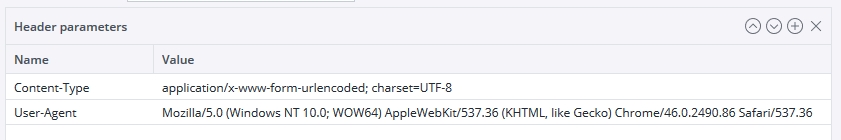
| Header parameters | The header parameters of the web service as parameter-value pairs. See screenshot below for an example: |
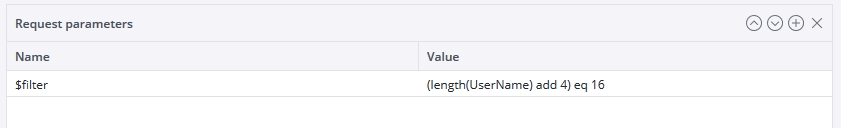
| Request parameters | The request parameters of the web service; required for GET method. The request parameter can be anything, as it is specific to the URL used. For example, the screenshot below shows a URL parameter to get a set of data specific to a certain location:
All request parameters are URL-encoded in REST connections and have to be provided without any encoding; so, for example, use the character "," instead of the corresponding encoded "%2C" one. Note that if the resource URL contains any request (query) parameters, it is not allowed to define additional request parameters in this section. This is the case, for example, with a resource URL set in the context of paging with a variable containing the nextlink URL. This restriction aims to avoid ambiguities, and not following it would lead to an error.
You can also deactivate / skip request parameters in a dynamic way without having them removed from your connection. While an empty parameter value would typically result in an error, you can set their value to |
| Authentication method | None: no authentication method required.
Basic: basic authentication for REST requests. Requires "User name" and "Password" specifications of the source. This method supports preemptive authentication. NTLM: NT LAN Manager Authentication Protocol (NTLM), a Microsoft security protocol used in Windows for authentication between clients and servers. It requires the "User name", "Password", "Workstation", and "Domain" specifications of the source. Token: refers to a separate connection of type OAuthToken, which handles tokens for OAuth2 authentication. See related article for possible limitations with this type of connection. |
| Request body | As an alternative to simple body parameters, the complete HTTP body can be specified here. This field is only used for the HTTP methods POST, PATCH, and PUT.
Note: if the connection is used in an XML/JSON load with a source, the request body will be filled dynamically and should therefore be left empty. |
| SSL mode | verify: checks the certificate; if response is OK, the certificate is validated.
trust: imports the certificate to the keystore, if not yet available. off: no SSL is used. |
| Timeout (in s) | The timeout of the web service request in seconds. |
| Ignore cookies policy | By default (unchecked), a warning ("Cookie rejected") appears when the HTTP call breaks a cookie policy. For example, this can be caused by an incorrect domain in the set-cookie header. The REST connection will nevertheless return a result.
If the option is checked, the warning will not appear. |
| Encrypted authorization header | Allows an HTTP authorization request header to be defined in an encrypted way, not visible in UI and logs. This can be done in 2 ways:
|
Note: One specific group of supported web services are those that fulfill the OData (Open Data) Protocol. For more information, see http://www.odata.org/.
Updated November 24, 2025