R is a free software programming language and software environment for statistical computing. It can be used for predictive analysis but also for a variety of other use cases. Jedox includes an RScript transform that executes an arbitrary script in R, based on the input data from one or several Jedox Integrator sources.
RScript transform represents the linkage between Jedox Integrator and the open-source statistical software R. Thereby, it is possible to operate any statistical calculation on one or several data sources within Jedox Integrator.
The RScript transform has four components:
- Data source
- External packages
- Name of result set
- RScript
External packages
The following R packages are available by default:
| Package | Title |
|---|---|
| car | Companion to Applied Regression |
| caret | Classification and Regression Training |
| keras | R Interface to 'Keras' |
| lpSolve | Interface to 'Lp_solve' v. 5.5 to Solve Linear/Integer Programs |
| lubridate | Dealing with Times and Dates |
| mlr | Machine Learning in R |
| reshape | Flexibly Reshape Data |
| rugarch | Univariate GARCH Models |
| skmeans | Spherical k-Means Clustering |
| smooth | Forecasting Using State Space Models |
| survival | Survival Analysis |
| tidyverse | Easily Install and Load the 'Tidyverse' |
| triangle | Provides the Standard Distribution Functions for the Triangle Distribution |
| tidymodels | Easily Install and Load the 'Tidymodels' Packages |
| tidyr | Create tidy data |
| xgboost | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
All dependent packages are also included. For details see https://cran.r-project.org/.
Contact Jedox Customer Portal regarding other external R packages.
Note: for security reasons, using BigQuery (packages and dependencies) on the R side is not supported.
Transform settings
| Data sources | An extract or transform for the corresponding Jedox Integrator project. Input is passed to RScript as a variable with the same name as the data source.
If no extract or transform are required, you must specify "Dummy" as the data source. |
| External packages | All external R-packages that are used in the RScript have to be declared here in a list. The packages listed above are not to be listed in the RScript code with the call of "library(....)", but to be added only in the "External packages" section. |
| Name of result set | The result of the calculation within the RScript must be a vector or a data frame, i.e., a list of vectors, factors, and/or matrices all having the same length. For Jedox Integrator to locate the result, the name of the variable containing the result has to be filled in here. |
| RScript | The code for the calculation composed in the R programming language has to be entered here. variables created in the Jedox Integrator project can be incorporated in the RScript as well. For further information about R language, visit http://cran.r-project.org/doc/manuals/r-release/R-lang.html. |
| Use caching | When checked (true), caching will be used; when not checked (false), caching will not be used. See Caching in Extracts and Transforms. |
| Guess types | When this option is set, value types in the R dataset containing the source data are automatically modified (guessed) by the R engine before the customized R scripting is processed in the RScript transform.
If not set, value types in the dataset are set explicitly based on the column types of the source in the RScript transform. |
Each line of the R script must be a complete command and subsequent lines must have the prefix "@".
Each RScript row should have only one R expression, which is generally the case in R. However, unlike the R console, there is no error returned if there are several expressions that are separated by spaces. For example, the expression xxxx a<-1 yyy returns no error.
If there are several valid expressions, only the first valid expression is executed. For example, there is no error for the expression x<-1 y<-1, but a value will only be assigned to x.
Multi-line statements
If a statement has multiple lines, then the following rules apply:
- After the first line, all subsequent lines belonging to the same statement (eg. for or while loop, if-else expression) should be prefixed with an "@" symbol.
- All for and while loops must be terminated with a ";" after the final "}". If-else statements do not need this.
- Other lines (e.g. within the body of statements) should be terminated with ";".
Examples: multi-line statements with for loop
Example 1:
for (row in rows){
@ new_val <- frame[frame$Row==row,];
@ for (r2 in rows2){
@ other_val <- frame[frame$Row==r2,];
@ if (new_val < 5){
@ frame$Level <- 0;
@ } else {
@ frame$Level <- 1;
@ }
@ };
@};Example 2:
for (row in rows){ new_val <- frame[frame$Row==row,]; for (r2 in rows2){ other_val <- frame[frame$Row==r2,]; if (new_val < 5){frame$Level <- 0;} else {frame$Level <- 1;}};};Example: calculating quantiles
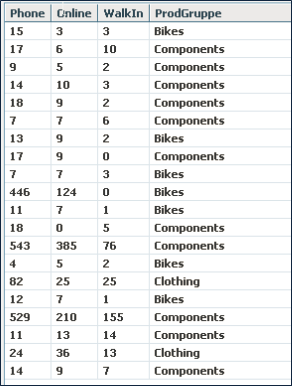
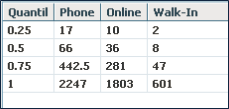
Input data: E_Cubedata
RScript:
Q<-c(0.25,0.5,0.75,1)
result <-
data.frame(Q,quantile(E_Cubedata$Phone,Q)quantile(E_Cubedata$Online,Q),quantile(E_Cubedata$walkIn,Q))
names(result) <-c("Quantil", "Phone", "Online", "Walk-In")Result:
Notes:
- The usage of R libraries / commands with graphical output is not supported in RScript transforms.
- For huge data volume, it is possible to allocate additional memory for the R engine. The R command memory.limit(<size>) requests a new memory limit in Mb. For example, to request a memory limit of 4000 Mb, you would enter memory.limit(4000)
- Automatic line completion (as in R Console) is not possible. This is especially relevant for IF and FOR statements.
While loop examples
while (i<=12}) {ProductType[i] <- levels(data$Product)[1]; i<-i+1}or
while (i<=12})
@{ProductType[i] <- levels(data$Product)[1];
@i<-i+1}See also Predictive Analytics and R Integration
Updated February 23, 2026