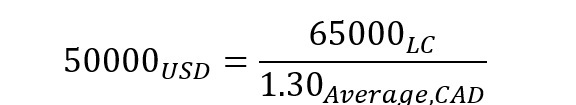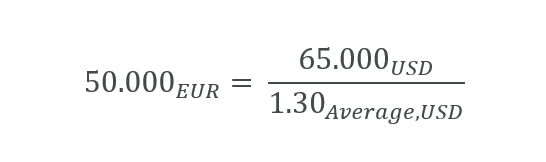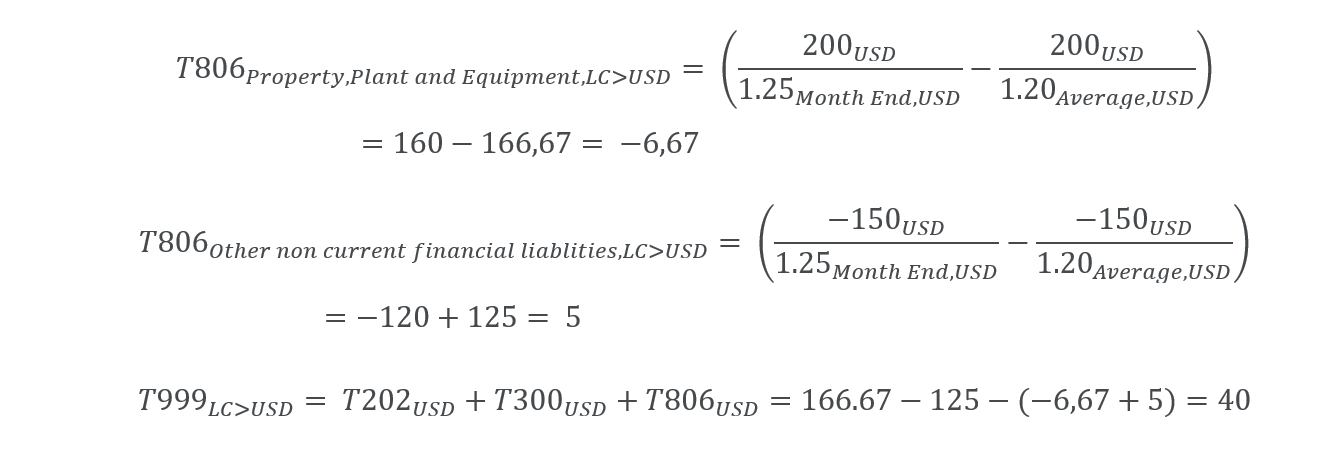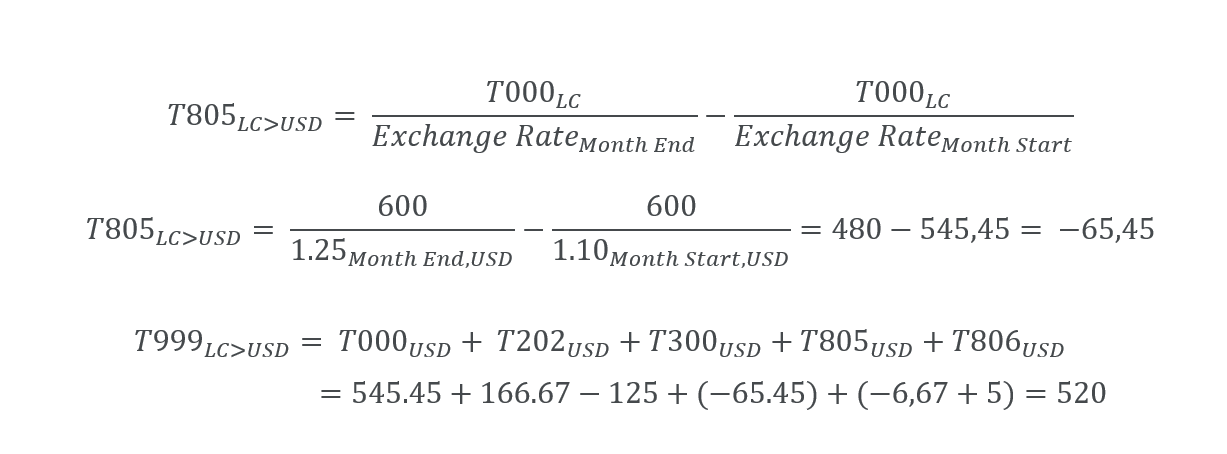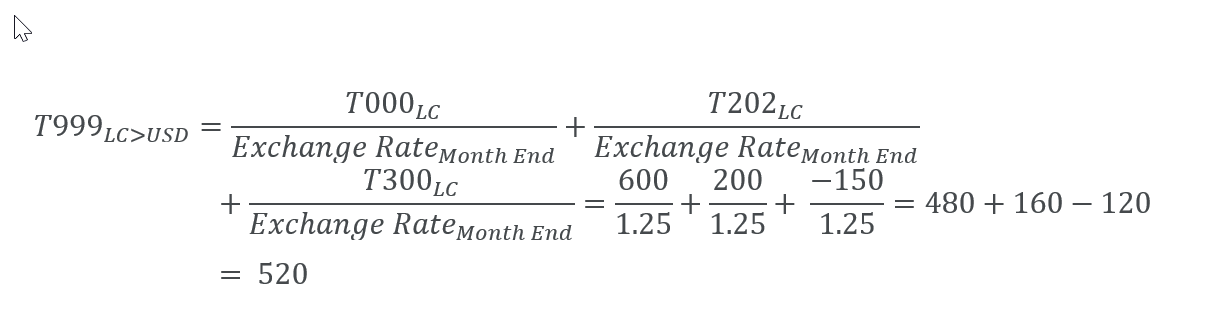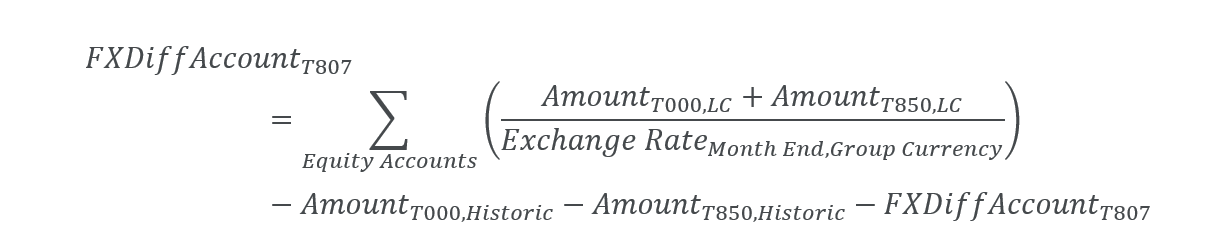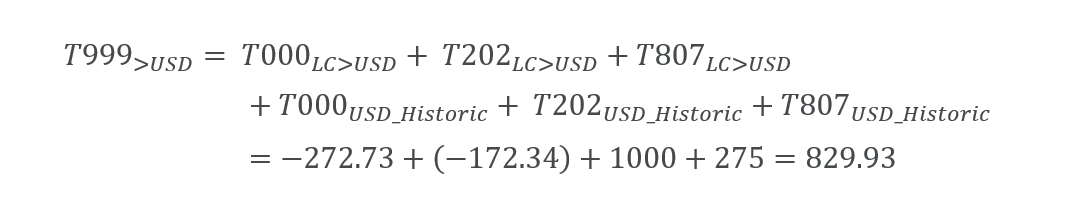Return to Financial Consolidation Model Overview
The currency conversion features the conversion of amounts stored in a local currency into a group currency or additional reporting currencies. The model can be configured for any set of local currencies and for one or multiple group currencies and additional reporting currencies.
The Financial Consolidation model performs the currency conversion in different ways - depending on the consolidation level, cube, account, transaction type or conversion type.
The different kinds of currency conversion are:
| Number | Name | Consolidation levels | Cubes | Accounts | Conversion types |
| 1 | Conversion from local currency into the group currency for movements | Local GAAP – Combined Financial Statement (Calculated) | Profit and Loss, Profit and Loss (Segment), Cash Flow and the Cash Flow (Segment) | All the accounts in the P&L and Adjustments in the cash flow | Average |
| 2 | Conversion from group currency into additional reporting currencies for movements | Combined Financial Statement – Consolidated Financial Statement (Adjusted) | Profit and Loss, Profit and Loss (Segment), Cash Flow and the Cash Flow (Segment) | All the accounts in the P&L and Adjustments in the cash flow | Average |
| 3 | Conversion of movements in Assets & Liabilities except for Investment account | Balance Sheet, Balance Sheet (Segment) | Movements on BS accounts with month end conversion | Average | |
| 4 | Conversion of opening balances in the Balance Sheet | Balance Sheet, Balance Sheet (Segment) | All the BS accounts except Equity. | Month Start | |
| 5 | Currency conversion of Equity | Balance Sheet cube | Historic |
The following transaction types are available to save different kinds of amounts:
-
There is a main hierarchy with
T000as the opening balance,T850and descendants to store movements,T801and descendants to store foreign exchange differences, andT999to save the closing balance. -
Second hierarchy for gross carrying amount with
T002as opening balance,T852and descendants to store movements,T802and descendants to store foreign exchange differences, andT992to save closing balance. -
Third hierarchy for accumulated depreciation and amortization with
T003as opening balance,T853and descendants to store movements,T803and descendants to store foreign exchange differences andT993to save closing balance. -
Fourth hierarchy for accumulated impairment with
T004as opening balance,T854and descendants to store movements,T804and descendants to store foreign exchange differences, andT994to save closing balance.
The calculation logic explanation uses the main hierarchy. For the parallel hierarchies, the same calculation logic is applied using the elements of each hierarchy accordingly.
1: Conversion from local currency into group currency for movements
Conversion from local currency into group currency for movements is done with the Average conversion type. This conversion applies to the Profit and Loss, Profit and Loss (Segment) cubes, and the adjustments in the Cash Flow and Cash Flow (segment) cubes. It is also restricted to the initial levels of the consolidation process, starting from Local GAAP to the Combined Financial Statement (calculated).
All of the above cubes include the following dimensions:
-
Version: This dimension is shared between the fact cube and theExchange Rates_YTDcube. -
Month_YTD: This dimension is shared between the fact cube and theExchange Rates_YTDcube. -
Legal Entity: TheCurrencyattribute in theLegal Entitydimension will be used to identify the actual currency code of the local currency for this entity. -
PnL AccountorCF Accountdimension: This dimension defines whichConversion Typeis used to select the exchange rate from theExchange Rates_YTDcube. We are using theConversion Typefrom theAccount. Usually, we useAverageconversion type. -
Currency: This dimension separates the input and output elements of the currency conversion. The table below defines the various elements of this dimension.
2. Conversion from group currency into additional reporting currencies for movements
Conversion from group currency into additional reporting currencies for movements is done with Average conversion type. This conversion applies to the Profit and Loss, Profit and Loss (Segment) cubes, and the adjustments in the Cash Flow and Cash Flow (segment) cubes.
These elements from the Currency dimension are applicable on this consolidation level:
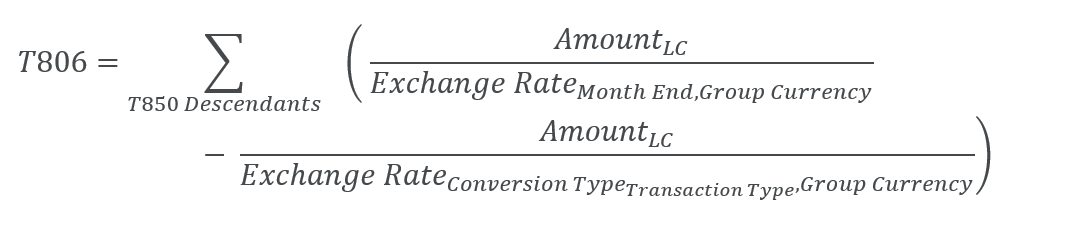
3. Conversion of movements in assets and liabilities
Conversion of movements in assets and liabilities is done on Average conversion type. This conversion applies to the Balance Sheet and Balance Sheet (Segment) cubes.
Example:
There are movements of 200 CAD on the T202 (Additions) and -150 CAD on the T300 (Decrease / Disposals) transaction type. Both are converted at an average rate of 1 USD = 1.20 CAD. The T000 (Opening) is assumed to be 0. The FXDiff element T806 must be computed so that T999 (Closing) shows the conversion at a month end rate of 1 USD = 1.25 CAD.
| Currency | BS Account | T000 - Opening | T202 - Additions | T300 - Decrease / Disposals | T806 - FXDiff, movements | T999 - Closing |
| LC(CAD) | Total Property, Plant and Equipment | 0.00 | -150.00 | -150.00 | ||
| Other non-current financial liabilities | 0.00 | 200.00 | 200.00 | |||
| LC > USD | Total Property, Plant and Equipment | 0.00 | -125.00 | 5.00 | -120.00 | |
| Other non-current financial liabilities | 0.00 | 166.67 | -6.67 | 160.00 | ||
We obtain the same value by converting closing balances into group currency on month end rate.
Parallel hierarchy for gross carrying amount uses T812 as foreign exchange differences element, and the movements are saved to T852 descendants and closing balance to T992.
Parallel hierarchy for accumulated amortization and depreciation uses T815 as foreign exchange differences element, and the movements are saved to T853 descendants and the closing balance to T993.
Parallel hierarchy for accumulated impairment uses T818 as foreign exchange differences element, and the movements are saved to T854 descendants and the closing balance to T994.
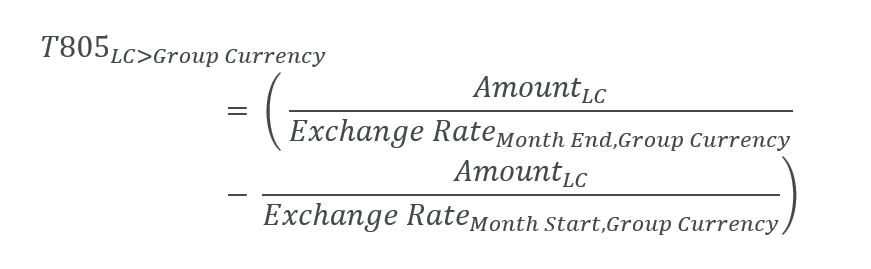
4. Conversion of opening balances in assets and liabilities
Conversion of opening balances in assets and liabilities is done on Month start conversion type. This conversion applies to the Balance Sheet and Balance Sheet (Segment) cubes.
Example:
There are openings of 600 CAD on the T000 (Opening) on Total Property, Plant and Equipment. The amount is converted at Month start rate of 1 USD = 1.10 CAD. The movements are as in the previous example. The FXDiff T805 element must be computed so that T999 (Closing) shows the conversion at a month end rate of 1 USD = 1.25 CAD.
| Currency | BS Account | T000 - Opening | T202 - Additions | T300 - Decrease / Disposals | T805 - FXDiff, opening | T806 - FXDiff, movements | T999 - Closing |
| LC(CAD) | Total Property, Plant and Equipment | 600.00 | -150.00 | 450.00 | |||
| Other non-current financial liabilities | 200.00 | 200.00 | |||||
| LC > USD | Total Property, Plant and Equipment | 545.45 | -125.00 | -65.45 | 5.00 | 360.00 | |
| Other non-current financial liabilities | 166.67 | -6.67 | 160.00 | ||||
We obtain the same value by converting closing balances into group currency on month end rate.
Parallel hierarchy for gross carrying amount uses T811 as foreign exchange differences element and T992 as closing balance.
Parallel hierarchy for accumulated amortization and depreciation uses T814 as foreign exchange differences element and T993 as the closing balance.
Parallel hierarchy for accumulated impairment uses T817 as foreign exchange differences element and T994 as the closing balance.
5. Currency conversion for accounts with historic conversion type
Currency conversion for equity accounts or any other balance sheet account with the historic conversion type in Balance Sheet, and Balance Sheet (Segment) cubes uses historic rates. (These are converted at the moment when the transaction took place).
Historic values are stored in the currency dimension on dedicated elements:
| …_Historic, e.g., USD_Historic | Captures amounts in the group currency or any additional target currency converted at historic rates. |
• Historic conversion rates are not stored in the model; instead, we store a pair of local currency and group currency values converted at the historic rates.
• Foreign exchange differences are computed on a separate account Reserve of exchange differences on translation under total equity. We are computing the difference between historic amount and conversion at the month end rate. We only use the Month End on Conversion type attribute for this FXDiff account. All equity accounts with historic currency conversion have one FXdiff account to compensate for the difference.
There can be other groups of accounts that use historic currency conversion and different FXDiff accounts.
• In case a historic value is available (input on xxx_Historic currency), no currency conversion takes place, and the closing balance uses the value input on xxx_Historic element. In case no historic amount has been input, the amount in local currency is converted with the Conversion type of the according transaction type. For transaction types with historic conversion type, the Average rate is used.
Example:
There are 500 CAD and 300 CAD on T000 (Opening) and 220 CAD on T202 (Additions). These amounts are saved to accounts with historic conversion type, on Issued capital, and on Retained earnings. Month start exchange rate is 1 USD = 1.1 CAD, and Average exchange rate is 1 USD = 1.2 CAD. The FXDiff T807 element must be computed so that T999 (Closing) shows the conversion at a month end rate of 1 USD = 1.25 CAD. The calculated amount is saved to account Reserve of exchange differences on translation.
| Currency | BS Account | T000 - Opening | T202 - Additions | T807 - FXDiff, historic | T999 - Closing |
| LC(CAD) | Issued capital | 500 | 500 | ||
| Retained earnings | 300 | 200 | 500 | ||
| Reserve of exchange differences on translation | |||||
| Total equity | 800 | 200 | 1,000.00 | ||
| USD_Historic | Issued capital | 625 | 625 | ||
| Retained earnings | 375 | 275 | 650 | ||
| Reserve of exchange differences on translation | |||||
| Total equity | 1000 | 275 | 0 | 1275 | |
| LC > USD | Issued capital | ||||
| Retained earnings | |||||
| Reserve of exchange differences on translation | -272.73 | -172.34 | -445.07 | ||
| Total equity | -272.73 | 0 | -172.34 | -445.07 | |
| >USD | Total equity | 727.27 | 275.00 | -172.34 | 829.93 |
We obtain the same value by combining closing balances in historic rate with exchange rate differences.
Parallel hierarchy for gross carrying amount uses T813 as foreign exchange differences element, and the movements are saved to T852 descendants and closing balance to T992.
Parallel hierarchy for accumulated amortization and depreciation uses T816 as foreign exchange differences element, and the movements are saved to T853 descendants and the closing balance to T993.
Parallel hierarchy for accumulated impairment uses T819 as foreign exchange differences element, and the movements are saved to T854 descendants and closing balance to T994.
Currency conversion does not apply
KPI’s like FTE and Headcount must not be currency converted. This can be configured by setting the Conversion Type attribute to ~. As an alternative, you also store such values on the XXX element in the Currency dimension.
Updated January 14, 2026